
“Copy That!” – Your Fun, Forensic Guide to Data Acquisition & Duplication 🕵️
Master the art of data acquisition with our take on EC-Council's Data Acquisition and Duplication module of their Digital Forensics Essentials certification. Learn the right way to duplicate digital evidence —bit by bit.
TL;DR 🧠
Data acquisition in forensics means capturing digital evidence exactly as it is—no fingerprints, no smudges. You’ll learn the different types of data acquisition, the tools used, and why the “image” isn’t something you post on Instagram. 📸💻
What is Data Acquisition in Digital Forensics?
Data acquisition is the process of collecting legally admissible digital evidence from devices—without modifying the original data.
It’s like catching a suspect red-handed… and then freezing them in carbonite for court. 🧊
Goals:
Integrity: Don’t touch or change the data. Ever.
Reproducibility: Others must be able to repeat the process and get the same result.
Preservation: Evidence must survive long enough to be examined, sometimes years later.
As forensic expert Harlan Carvey puts it:
“The integrity of the data is your reputation. If you corrupt it, you might as well be wearing a ski mask in court.”
📚 Windows Forensic Analysis Toolkit, 4th Ed. – Carvey, 2014
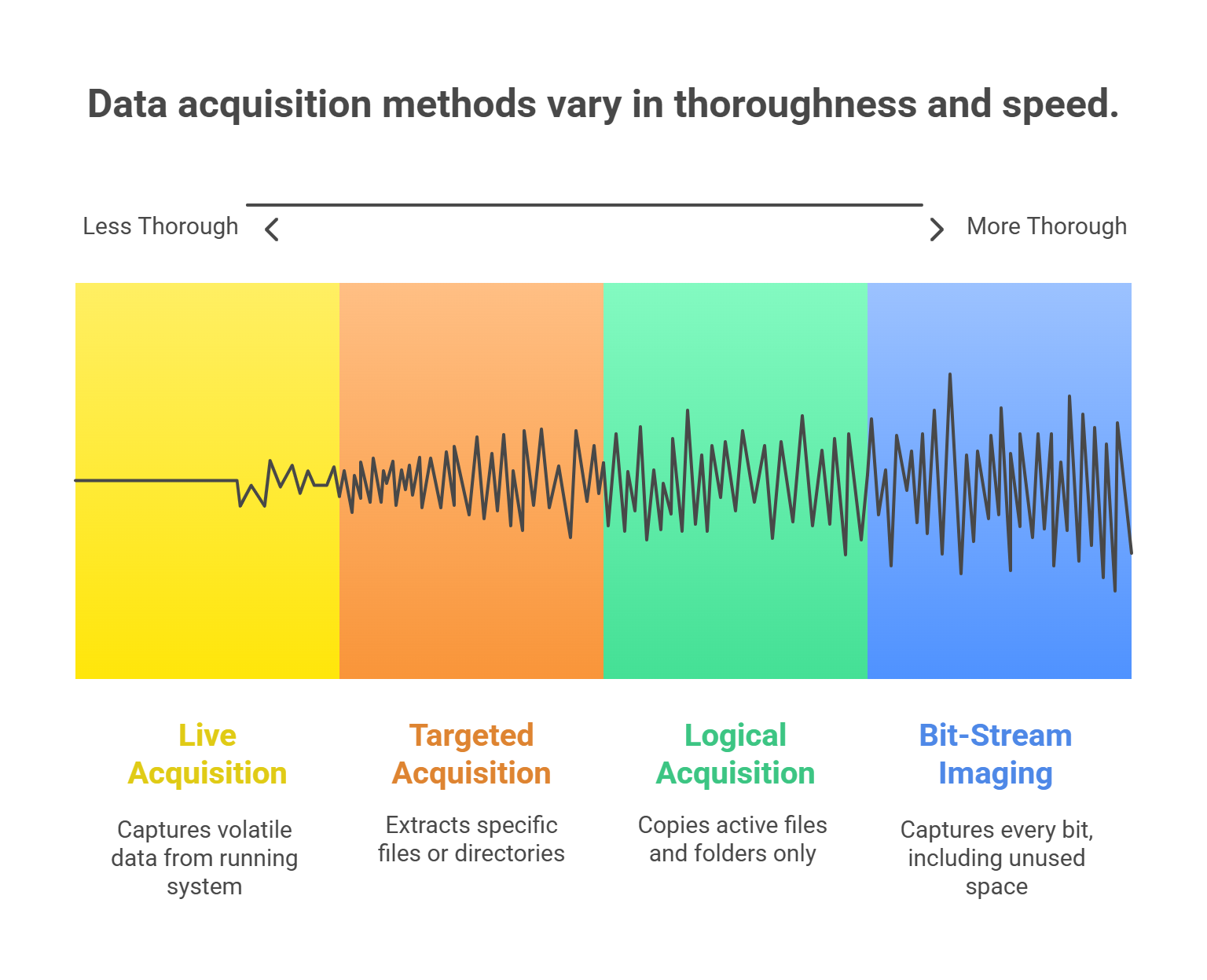
Types of Data Acquisition (a.k.a. Four Flavors of "Copy Everything Carefully")
1. Bit-Stream Imaging (Full Disk Image)
Captures every bit—used AND unused space.
Most thorough.
Needed if you want to recover deleted files or hidden partitions.
🔍 Forensics gold standard.
2. Logical Acquisition
Grabs active files and folders only (visible to OS).
Faster but less thorough.
Good for massive systems when time is limited.
3. Targeted Acquisition
Focuses on specific file types or directories (like just pulling emails or PDFs).
Useful for triage or court-ordered searches.
⚖️ May avoid unnecessary personal data grabs.
4. Live Acquisition
Used when the system is running.
-
Necessary when:
Encryption is enabled (can't access once shut down).
Volatile data (RAM) is critical (e.g., password dumps).
Risky: changes are being made as you collect data. Handle with care—like defusing a bomb wearing oven mitts. 😬

Data Acquisition Formats: E01, AFF, and Raw (Not the WWE Kind)
📦 RAW (.dd or .img)
Sector-by-sector copy.
Open and universal.
Large file size, but zero compression = cleaner data.
🧩 E01 (EnCase Evidence Format)
Compressed.
Includes metadata and hash verification.
Supported by forensic tools like EnCase, FTK.
💡 AFF (Advanced Forensic Format)
Open-source alternative to E01.
Includes metadata, supports compression and encryption.
Toolkits that make it happen:
FTK Imager
EnCase Forensic
Guymager (Linux-friendly)
dc3dd (for command-line warriors)
Each format includes hash values (MD5, SHA1) to confirm data integrity—because “close enough” only counts in horseshoes and hand grenades.
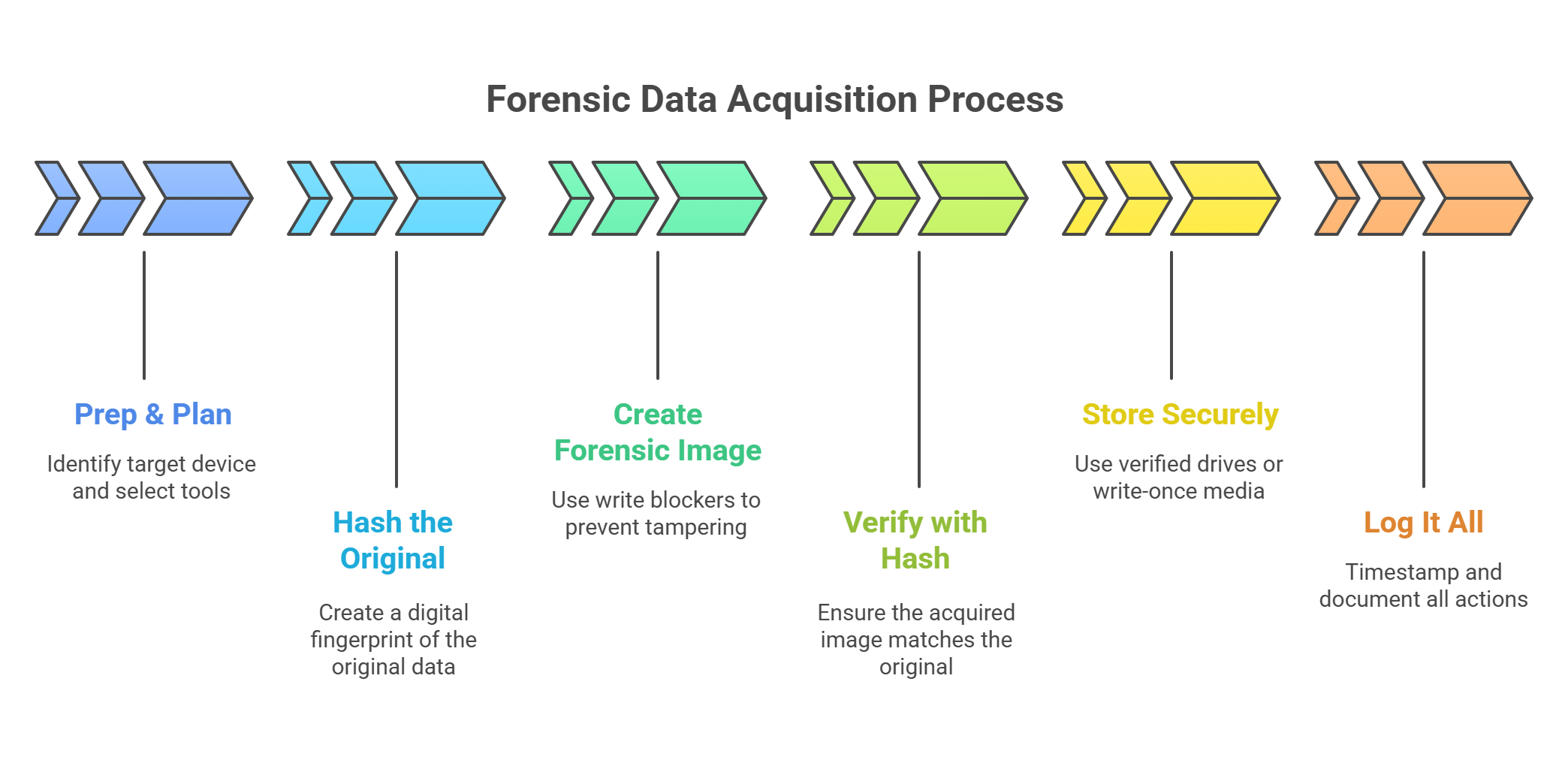
Forensic Data Acquisition Methodology (CSI: Cyber, But Make It Real)
🧪 Step-by-Step Process:
-
Prep & Plan
Identify the target device.
Select tools and format.
Document everything. (Chain of custody matters!)
-
Hash the Original
Hash before acquisition to get a digital fingerprint.
Think of it like sealing the evidence with invisible ink.
-
Create Forensic Image
Use write blockers to prevent tampering.
Perform bit-stream copy or logical image, as needed.
-
Verify with Hash
Hash the acquired image.
It must match the original. No match = throw it out.
-
Store Securely
Use verified drives or write-once media.
Backup. Then backup your backup.
-
Log It All
Timestamp everything.
List tools, settings, and file names used.
You’ll thank yourself when the cross-examination starts.
TL;DR Recap: "Don’t Just Copy—Clone It Like a Pro" 🧬
Bit-stream imaging is king—get everything, even deleted stuff.
Know when to use logical or live acquisition (but tread carefully).
Use trusted formats (RAW, E01, AFF) and hash everything.
Document like your career depends on it—because it does.
Trust your tools, verify your data, and never touch the original.
Looking for More Digital Sleuthing Skills?
Crack open more of our EC-Council DFE blog series to turn every byte into a breadcrumb trail.
📺 You'll see how data is cloned, analyzed, and presented in court like a boss.
Tags: Digital Forensics, EC-Council DFE, Data Acquisition, Forensic Duplication, Evidence Imaging, Disk Cloning, Computer Forensics
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment