What is RAM? And Why Should I Care? (Hint: It Makes Your Computer Zoom!)
Ever wondered what that "RAM" thing is all about when you're trying to install a new game or upgrade your operating system? It's not just some random tech jargon—RAM (Random Access Memory) is the VIP backstage pass for your computer's performance. Let's dive in and demystify this essential component!
RAM 101: The Short-Term Memory of Your Computer
Think of RAM like your computer's short-term memory. When you open an app, load a document, or stream a video, all that information gets temporarily stored in RAM. It's the super-fast holding area that allows your CPU (the brain of your computer) to access and process data quickly. The more RAM you have, the more tasks your computer can juggle smoothly without slowing down. No more frustrating lag or endless spinning wheels of doom!
Dynamic RAM (DRAM) and Static RAM (SRAM)
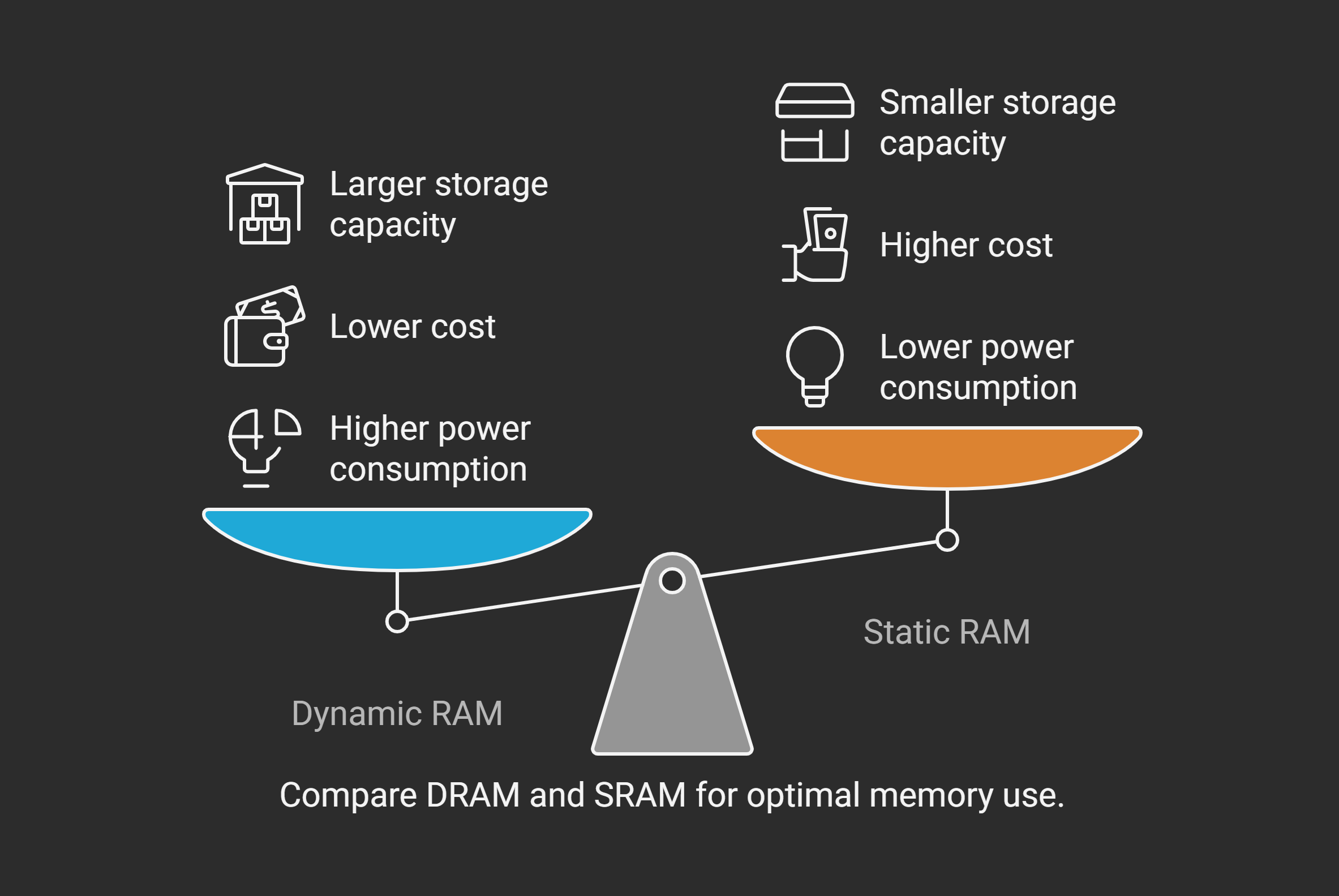
Dynamic RAM (DRAM) and Static RAM (SRAM) are two different kinds of memory used in computers and other gadgets. DRAM is made up of tiny cells, each with a capacitor and a transistor. These cells need to be refreshed constantly to keep the information alive, which uses more power, but DRAM can store a lot and is cheaper.
On the other hand, SRAM has a special kind of circuitry that doesn't need refreshing, so it's faster than DRAM. However, SRAM costs more and takes up more space, so it's not great for storing a lot of data. DRAM is usually used for the main memory in computers because it's affordable and can hold a lot, while SRAM is used for cache memory where speed is really important.
DIMMs and SO-DIMMs: The Memory Modules That Make it Happen
The actual RAM chips live on these cool little things called DIMMs (Dual In-Line Memory Modules). They slot right into your motherboard and come in different sizes and speeds.
DIMMs:
These are the standard-sized memory modules you find in desktop computers.
SO-DIMMs:
Short for "Small Outline DIMM," these are the compact versions designed for laptops and other space-conscious devices.
Think of it like this: DIMMs are the comfy king-size beds of the memory world, while SO-DIMMs are the cozy, efficient twin beds.
DDR: Double Data Rate - Double the Fun?
You've probably heard terms like DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5 thrown around. DDR stands for "Double Data Rate," and it refers to how quickly data can be transferred to and from the RAM. Each new generation of DDR is faster than the last, meaning your computer can access information quicker and process tasks more efficiently. It's like upgrading from a bicycle to a sports car—you'll get where you need to go much faster!

The Need for Speed (and Compatibility)
Just like trying to fit a square peg into a round hole, you can't just use any old RAM in your computer. Those little notches (or "keys") on the DIMMs ensure you install the right type of memory for your motherboard. Trying to force an incompatible module is like trying to speak Klingon to your dog—it just won't work!
The Bottom Line: RAM Matters!
RAM is the unsung hero of your computer's performance. It's the crucial ingredient that lets you multitask like a pro, game without lag, and enjoy a smooth, responsive computing experience. So, next time you're feeling the need for speed, remember the power of RAM!
FAQ: All About Computer Memory
What uses a lot of RAM?
Several types of applications and activities consume significant amounts of RAM:
Virtual machines and emulation software
Video editing and 3D rendering applications
Modern gaming, especially open-world titles with high-resolution textures
Web browsers with multiple tabs open (each tab can use 100MB-1GB)
Code compilation and integrated development environments (IDEs)
Photo editing software when working with large or multiple files
Database operations and data analysis tools
CAD software for engineering and design
Is 32GB RAM overkill?
Whether 32GB of RAM is overkill depends entirely on your use case:
For basic users (web browsing, document editing, streaming): Yes, 32GB is more than needed; 8-16GB is typically sufficient
For gamers: Usually more than necessary, but beneficial for simulation games, heavily modded titles, or gaming while running background applications
For content creators: Not overkill for video editors, 3D modelers, or those running multiple creative applications simultaneously
For developers: Appropriate for running virtual machines, containers, and development environments
For future-proofing: 32GB provides headroom for increasing software requirements over the next few years
How much does 8GB RAM cost?
As of March 2025, the cost of 8GB RAM varies based on type, speed, and brand:
DDR4: Typically $25-45 for a single 8GB stick
DDR5: Approximately $40-70 for a single 8GB stick
Laptop RAM: Usually $30-60 depending on form factor
Server RAM: Generally more expensive, starting around $60-100
Apple/Mac RAM: Premium pricing, often 30-50% higher than standard modules
Prices may vary based on your region, sales, and availability.
What happens if I use 100% of my RAM?
When RAM usage reaches 100%, several problematic behaviors occur:
Slowdown: Your system becomes noticeably sluggish as it struggles to manage memory
Page file/swap usage: The operating system begins using storage drives as virtual memory, which is significantly slower than RAM
Application lag: Programs may freeze temporarily or become unresponsive
Potential crashes: Applications may crash as they fail to allocate required memory
System instability: In extreme cases, the entire system may freeze or crash
Automatic closing of applications: Some operating systems may force-close background applications
What is eating up all my RAM?
Common culprits for high RAM consumption include:
Web browsers (especially Chrome) with numerous tabs and extensions
Background services and startup applications
Memory leaks in poorly optimized software
Antivirus scans running in the background
System caching (not necessarily problematic as the OS will free this when needed)
Windows/macOS system processes
Modern games, particularly those with large, detailed worlds
Creative applications like Adobe Photoshop, Premiere Pro, or Blender
You can identify RAM-hungry applications using Task Manager (Windows), Activity Monitor (Mac), or top/htop (Linux).
What reduces RAM usage?
To lower your system's RAM consumption:
Close unused applications and browser tabs
Disable unnecessary startup programs
Use lightweight alternatives to RAM-intensive software
Manage browser extensions and remove unused ones
Update your operating system and applications to benefit from memory optimizations
Adjust virtual memory settings to optimize swap file usage
Restart your computer periodically to clear accumulated memory usage
Scan for malware which may be consuming resources in the background
Is upgrading RAM worth it?
Upgrading RAM is worth it in these scenarios:
Your system regularly reaches 70-80% memory usage during normal tasks
You experience slowdowns when multitasking or running demanding applications
You plan to use memory-intensive applications like video editors or virtual machines
You're experiencing frequent crashes related to memory shortages
You want to future-proof your system for upcoming software requirements
RAM upgrades typically provide more noticeable performance improvements than other upgrades when memory is the bottleneck in your system.
What is the disadvantage of 32GB RAM?
The primary disadvantages of 32GB RAM include:
Cost: Higher upfront expense for memory you might not fully utilize
Power consumption: Slightly increased electricity usage (though minimal)
No performance benefit if your workloads never use more than 16GB
Potential compatibility issues with older motherboards or systems
Opportunity cost: Money that could be spent on other components like a better CPU or GPU
For most users, these disadvantages are minor compared to the benefits of having additional memory headroom.
How much better is DDR5 than DDR4?
DDR5 offers several improvements over DDR4:
Higher bandwidth: Typically 50-60% more throughput in real-world applications
Better power efficiency: Lower operating voltage (1.1V vs 1.2V for DDR4)
Higher maximum capacity per memory module
Improved error correction capabilities
Higher base frequencies: Starting at 4800 MHz compared to DDR4's 2133 MHz
However, DDR5 also has some considerations:
Higher latency: Though compensated by higher frequencies
More expensive: 30-50% price premium over equivalent DDR4 modules
Requires newer hardware: Only compatible with newer motherboards and CPUs
Diminishing returns: Not all applications benefit significantly from the increased bandwidth
For gaming and mainstream use, the real-world performance difference is currently around 5-15%, depending on the specific application and system configuration.
Mike G.
IT Certification Jump
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



