
The Legal Loopholes, Landmines, and Laughs: A PenTester's Guide to Not Going to Prison
Remember when you were a kid and thought being a "hacker" meant wearing cool sunglasses indoors while typing frantically on a keyboard? Turns out, the reality involves a lot more paperwork and a lot less dramatic lighting. Welcome to the world of ethical hacking, where permission slips are your best friend!
When "Breaking In" Becomes a Career Path
Imagine being paid to break into systems, find weaknesses, and exploit vulnerabilities—all without the inconvenience of a SWAT team breaking down your door at 3 AM. That's the life of an ethical hacker conducting penetration tests. But there's a crucial difference between you and the cybercriminals featured in your favorite hacker movies: permission.
As the great philosopher Uncle Ben once said, "With great power comes great responsibility." In penetration testing, that responsibility is protected by a web of legal documents, ethical guidelines, and professionally agreed-upon boundaries that would make even the most dedicated bureaucrat smile with approval.
The ROE: Your "Get Out of Jail Free" Card
The Rules of Engagement (ROE) document is essentially your permission slip to do what would otherwise be highly illegal activities. Think of it as the difference between being a locksmith who's been hired to open a door and someone trying to break into a house at midnight with a crowbar and a suspicious duffel bag.
What Your ROE Should Include:
Scope definition: Exactly which systems you can test (IP ranges, domains, applications)
Timing: When you can conduct tests (usually during low-traffic periods)
Methodology: What techniques are permitted and which are off-limits
Communication protocols: Who to contact if something goes wrong
Data handling: How discovered data should be managed and protected
Real-World ROE Horror Story: The "Oops" Heard Around the Company
Consider the case of a penetration tester I'll call "Dave" (not his real name, for reasons that will become obvious). Dave was hired to test a company's network security but failed to get explicit scope clarification about their cloud infrastructure. When he discovered and accessed a cloud database he thought was in-scope, he accidentally triggered a production outage that cost the company thousands of dollars per minute.
The problem? That particular database wasn't actually included in his testing authorization. Despite his good intentions, Dave found himself in a legal gray area because the ROE wasn't specific enough. The company ultimately didn't press charges, but Dave's firm had to pay for damages, and his reputation took a significant hit.
The lesson: A vague ROE is like trying to perform surgery with oven mitts on—technically possible, but unnecessarily risky and likely to end badly for everyone involved.

Legal Frameworks: The "Choose Your Adventure" Book Nobody Wants to Read
Different jurisdictions have different laws regarding computer access, and ignorance of these laws won't protect you. Here's a speed-run through some major legal considerations:
United States: The CFAA (Computer Fraud and Abuse Act)
The CFAA is the big one in the U.S. Enacted in 1986 (when computers were basically fancy calculators), this law has been updated to address unauthorized access to protected computers. Violations can result in up to 10 years in prison for first offenses.
European Union: GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
GDPR focuses on data privacy rather than system access specifically, but it adds another layer of compliance requirements. If you discover personal data during your pentest, you're subject to strict handling requirements.
California: CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act)
Similar to GDPR but with a California twist, the CCPA imposes additional requirements for handling discovered personal data during penetration tests of California-based companies or systems containing California residents' data.
The Penetration Tester's Ethical Compass
Ethics in pentesting go beyond legal compliance. Just because you can do something doesn't mean you should. These principles align directly with the "Planning and Scoping" domain in the CompTIA PenTest+ certification:
Do No Harm: The Hippocratic Oath applies to systems too
Minimal Invasion: Use the least intrusive method necessary
Data Protection: Treat discovered data as highly confidential
Transparent Reporting: Document everything—the good, the bad, and the ugly
Professional Development: Stay updated on new threats and ethical standards
The Art of Staying In Scope: A Delicate Dance
Staying within scope during a penetration test is like walking a tightrope while juggling flaming torches—challenging but necessary for your continued wellbeing.
The Temptation of Scope Creep
Imagine you're testing a web application and discover a vulnerability that could potentially lead to accessing another system not mentioned in your ROE. The curious hacker in you wants to follow that thread to see where it leads. The professional ethical hacker in you should recognize this as a scope boundary.
Instead of exploiting that vulnerability to access the out-of-scope system, the correct approach is to:
Document the potential pivot point
Report it as a finding
Recommend a scope expansion if necessary
Get written approval before proceeding
When In Doubt, Reach Out
If you're ever uncertain whether an action might exceed your authorized scope, stop and contact your designated point of contact. A five-minute conversation can save you from potentially years of legal headaches.

The "Get Out of Jail" Checklist
To ensure your penetration testing activities remain on the right side of legal and ethical boundaries, use this handy checklist:
✅ Obtain written authorization before testing begins
✅ Verify scope boundaries are clearly defined
✅ Ensure emergency contacts are established
✅ Document all testing activities meticulously
✅ Handle discovered data according to agreed protocols
✅ Report all findings, even if they seem minor
✅ Get explicit permission before expanding scope
✅ Maintain confidentiality about discovered vulnerabilities
Certifications: Your Badge of Ethical Authority
The CompTIA PenTest+ certification specifically tests your knowledge of legal and ethical considerations. When preparing for this exam, pay special attention to the "Planning and Scoping" domain, which covers:
Legal compliance requirements
Rules of engagement documentation
Scope definition and limitations
Communication and escalation procedures
Data handling protocols
Other valuable certifications that emphasize ethical hacking practices include:
Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)
GIAC Penetration Tester (GPEN)
Data Privacy: The Extra Layer of Responsibility
When conducting penetration tests, you may encounter sensitive data including:
Personal identifiable information (PII)
Protected health information (PHI)
Payment card information (PCI)
Intellectual property
Under regulations like GDPR and CCPA, even authorized access to this data comes with strict handling requirements. Your test documentation should include specific protocols for:
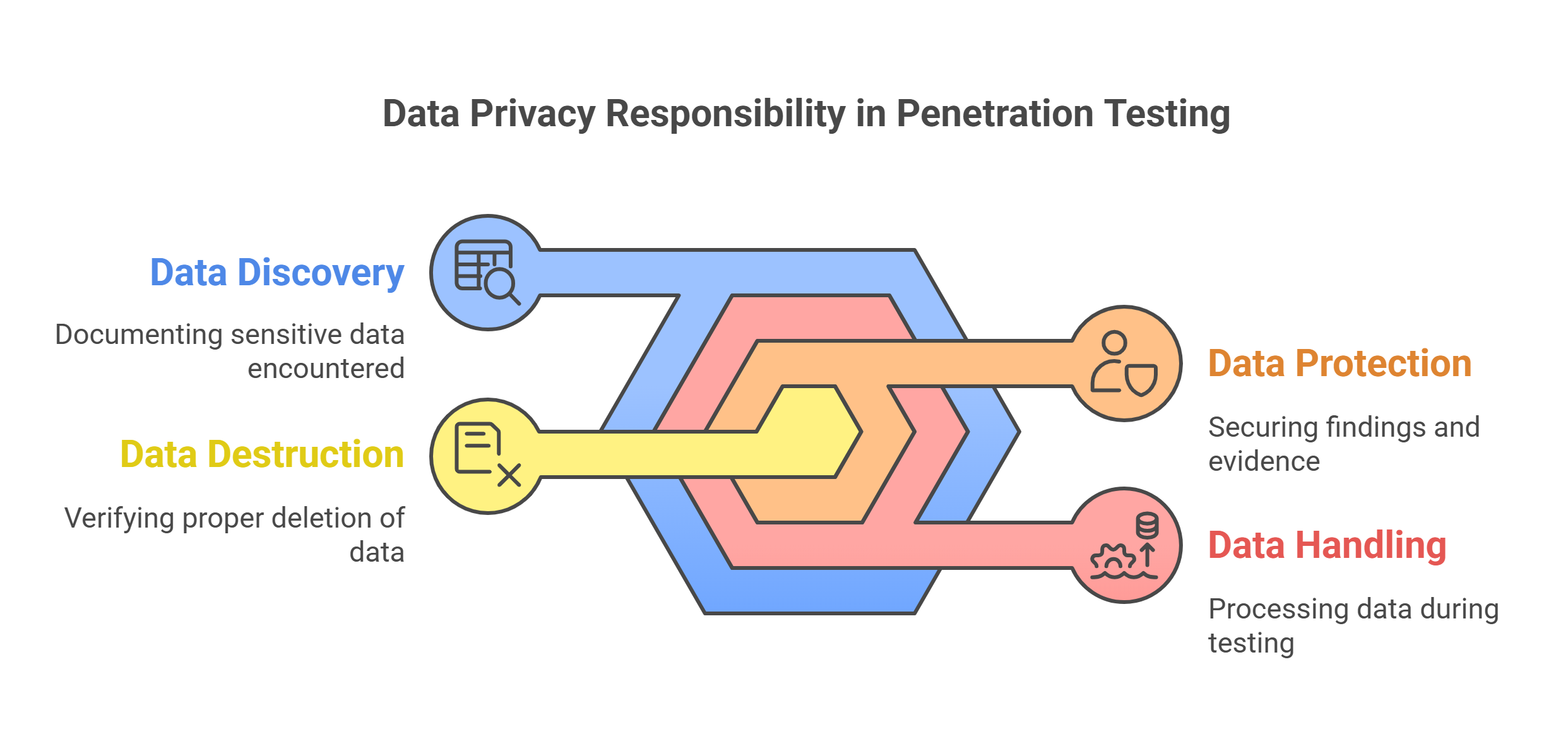
Data Discovery: Documenting what sensitive data was encountered
Data Handling: How the data was processed during testing
Data Protection: Measures taken to secure any findings or evidence
Data Destruction: Verification that data was properly deleted after testing
Case Study: The Epic Fail of "Helpful" Harry
Let's examine a real-world scenario gone wrong: A penetration tester (we'll call him "Helpful Harry") was testing a healthcare organization's patient portal. The scope clearly stated that actual patient records were off-limits, but Harry discovered a vulnerability that exposed patient data.
Instead of simply documenting the vulnerability, Harry decided to "help" by downloading several patient records to demonstrate the severity of the issue. His intentions were good—he wanted to show exactly what data was at risk—but his actions violated:
The Rules of Engagement
HIPAA regulations
State privacy laws
Basic ethical principles
The result? The healthcare organization reported the violation to authorities, Harry faced potential criminal charges, and his company lost the client and faced significant reputation damage.
The correct approach would have been to:
Document the vulnerability
Capture screenshots showing the type of data exposed (without capturing actual records)
Immediately report the issue to the designated contact
Let the client decide how to proceed
TL;DR: The PenTester's Prime Directive
Get clear written permission before you touch anything
If it's not in scope, it doesn't exist to you
Document everything as if your freedom depends on it (because it might)
When in doubt, ask before you act
Treat discovered data like radioactive material—handle with extreme care
Ready to Dive Deeper?
Congratulations! You've completed your crash course in "How to Hack Legally Without Becoming Someone's Prison Pen Pal."
Be sure to check out our next article, "AI vs. PenTester: How Artificial Intelligence is Changing the Penetration Testing Landscape (and What PenTest+ Pros Need to Know)"
Don't forget to share this article with that friend who still thinks "hacking" means wearing a black hoodie and typing really fast. Hope you come back soon!
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment