
Encrypting Data: Making Hackers Cry Since the Dawn of Cyberspace – CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 (1.4) 💾
Understand data encryption like a pro. This CompTIA Security+ 701 article covers transport & database encryption, cryptographic keys, and more—in plain English with relatable, scannable fun.
TL;DR (Too Long; Data’s Risky!)
Encryption is how we protect sensitive data from digital creepers. It scrambles readable information into gibberish unless you’ve got the right cryptographic key to unlock it. This blog breaks down the different ways we encrypt data in motion (transport), at rest (like databases), and everywhere in between. Whether you’re securing a Google Doc or locking down a government database—encryption is the name of the game 🔐.
🕵️♂️ So, What Is Data Encryption Anyway?
Data encryption is the process of converting plaintext (normal words) into ciphertext (word salad) using cryptographic algorithms and keys. Without the correct key? Good luck decoding that gibberish—unless you're a quantum computer (and even then... it's iffy).
"Encryption is the last line of defense. When everything else fails, your data should still be unreadable to the attacker."
— Bruce Schneier, world-renowned cryptographer and author of numerous IT security books.
🧠 Types of Encryption You Shouldn’t Sleep On
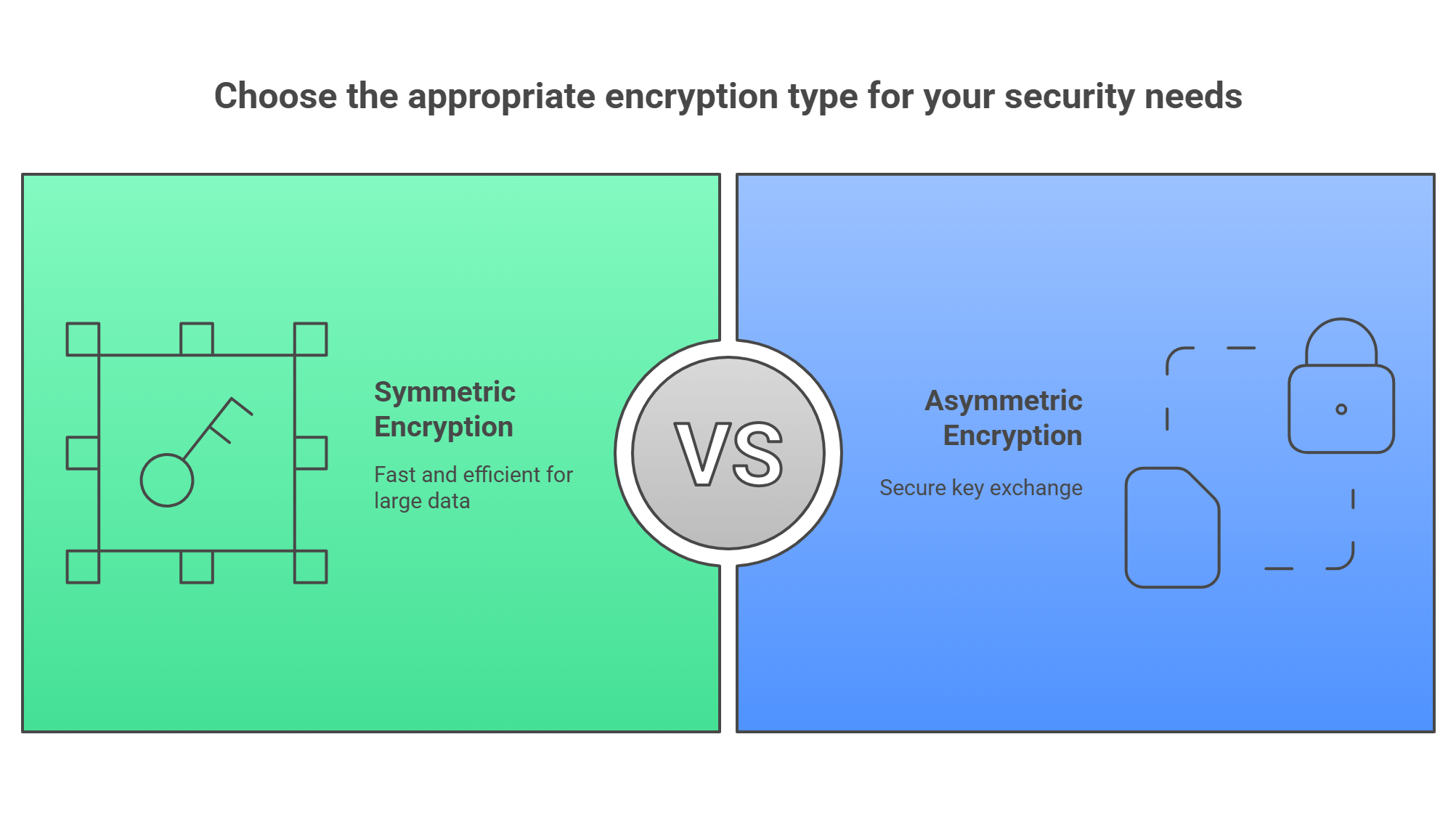
Symmetric Encryption
Same key encrypts and decrypts
Fast and efficient
Ideal for encrypting large amounts of data (like database files)
Asymmetric Encryption
Key pair (public & private)
Slower, but perfect for securing key exchanges
Often used to start encrypted sessions before handing off to symmetric keys for speed
These two often work together like a buddy-cop duo. Asymmetric sets up the safe house. Symmetric handles the daily security.
🚀 Transport Encryption: Keeping Data Safe in Transit ✈️
Think of transport encryption as the armored truck for your data.
Used when:
You send an email
Browse a website
Use an API
The goal: Prevent eavesdropping or tampering during transmission
Real World Examples:
TLS (Transport Layer Security): The real MVP behind that HTTPS lock icon
VPN (Virtual Private Network): Your encrypted tunnel through the Wild West of Wi-Fi
SSH (Secure Shell): For logging into servers like a pro without leaking your credentials
“Without TLS, the modern web wouldn’t exist as we know it.”
— Troy Hunt, Microsoft Regional Director and creator of Have I Been Pwned
🧱 Database Encryption: Locking Down the Vault
Encrypting the database is like sealing your digital journal in a steel vault with biometric locks—and then hiding the vault behind a bookshelf that only opens if you quote a line from The Matrix.
Why it matters:
Protects data at rest (when it’s not moving)
Shields from insider threats and physical theft
Helps meet compliance standards (HIPAA, GDPR, PCI DSS, etc.)
Two Main Methods:
Transparent Data Encryption (TDE): Automatically encrypts data at the storage level
Column-Level Encryption: Encrypts specific fields, like credit card numbers or SSNs
Tools & Tech:
Microsoft SQL Server TDE
MySQL's
AES_ENCRYPT()Oracle Advanced Security
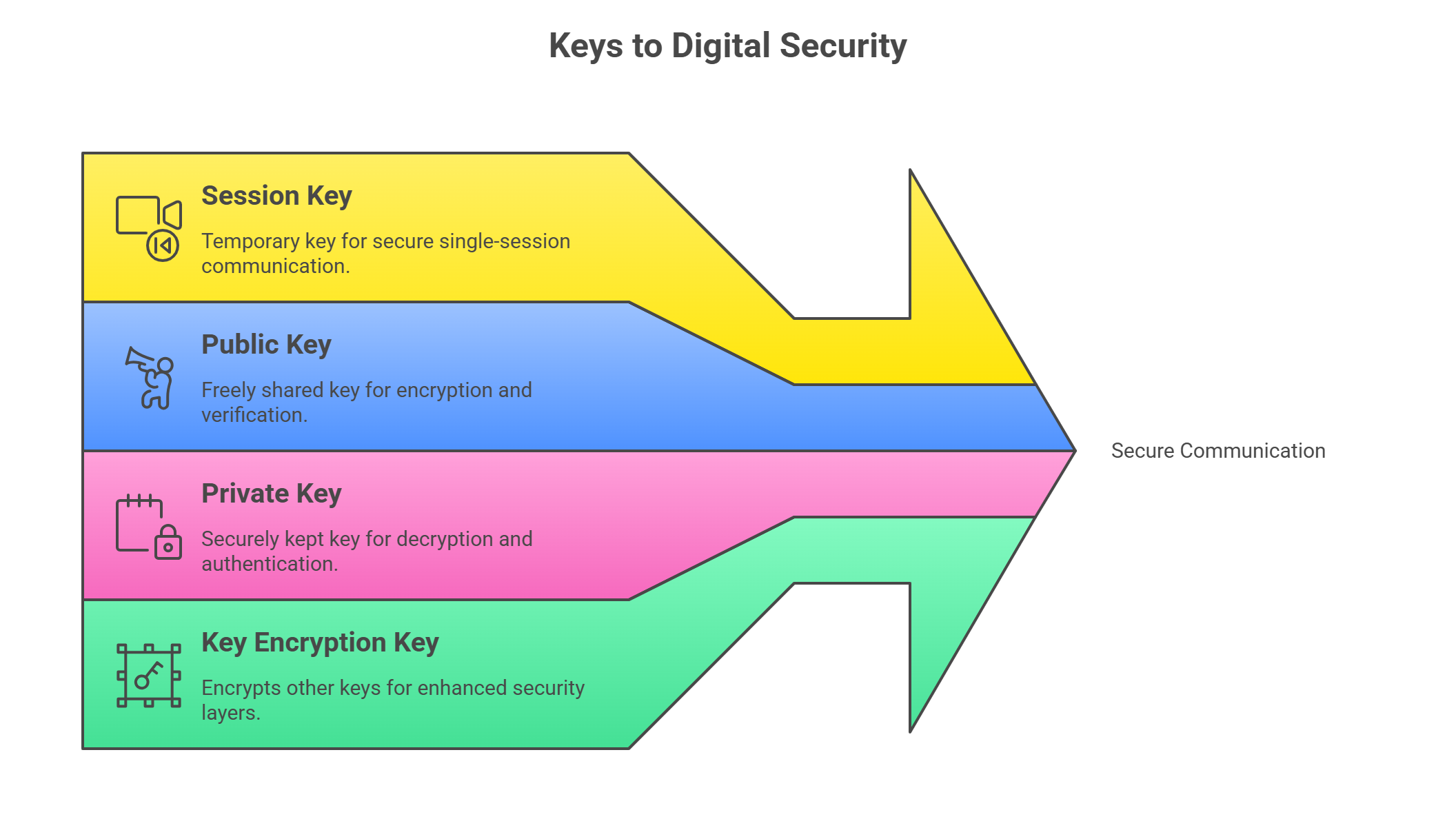
🔑 Cryptographic Keys: The Secret Sauce of Encryption
A cryptographic key is like the password to unscramble the secret message—except it’s way more complex and not written on a sticky note.
Types You’ll See in the Wild:
Session Key: Temporary, used for a single session (often symmetric)
Public Key: Part of a key pair (shared freely)
Private Key: Also part of a key pair (kept safe and secure)
Key Encryption Key (KEK): Used to encrypt other keys (yes, that’s a thing)
“The strength of your encryption doesn’t just depend on the algorithm—it depends on how well you protect your keys.”
— CompTIA Security+ Study Guide, by Mike Chapple
🔁 Key Management: The Most Underrated Superpower
Poor key management is like hiding your house key in a flower pot and then posting about it on Instagram.
Best Practices:
Use a Key Management System (KMS) like AWS KMS or Azure Key Vault
Rotate keys regularly
Never hardcode keys into your source code (seriously, don’t)
🛡️ Full Disk Encryption vs. File-Level Encryption
Encryption Type |
What It Protects |
Good For |
|---|---|---|
Full Disk Encryption (FDE) |
Everything on the storage device |
Laptops, desktops, mobile devices |
File-Level Encryption |
Specific files or folders |
Cloud storage, shared folders |
Combine them for max paranoia and peace of mind 😎.
🔄 Real-World Encryption Use Cases
HTTPS Websites: Your browser uses TLS to talk to secure sites
Online Banking Apps: Encrypt everything from login to logout
Medical Records: Must be encrypted under HIPAA law
Cloud Storage: Providers encrypt files at rest and in transit
Basically, if it contains private info and it’s not encrypted… we’ve got problems.

TL;DR Redux
Data encryption keeps information safe from unauthorized access
Transport encryption secures data in motion (TLS, VPN, SSH)
Database encryption secures data at rest (TDE, column-level)
Cryptographic keys are essential—guard them with your life
Key management = seriously underrated
Encryption is everywhere, from your texts to your taxes
Final Thoughts: Encrypt It or Regret It
In a world where one click can leak millions of records, encryption isn’t optional—it’s survival. Whether you’re sending sensitive client data or just want your playlist to stay between you and your algorithm, encryption is the cyber seatbelt that keeps you from flying through the digital windshield.
Call to Action: Stay Safe, Stay Encrypted
Liked this explainer?
➡️ [Catch more Security+ SY0-701 breakdowns and walkthroughs right here on ITCertificationJump —fun, fast, and 100% exam-ready.]
Thank you for reading.
Security+, SY0-701, Data Encryption, Cryptographic Keys, Database Encryption, Transport Encryption, Cybersecurity Basics, Encryption Explained, IT Certification, InfoSec, Study Guide
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment